WBJEE- Physics & Chemistry-2011 (Eng)
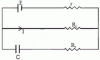
1. The charge on the capacitor of capacitance C shown in the figure below will be

(A) CE (B) CER1R1+r (C) CER2R2+r (D) CER1R2+r
2. The resistance across A and B in the figure below will be
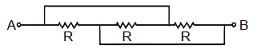
(A) 3R (B) R (C) R3 (D) None of these
3. Five equal resistance, each of resistance R, are connected as shown in figure below. A battery of V volt is connected between A and B. The current flowing in FC will be
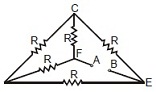
(A) 3VR (B) VR (C) V2R (D) 2VR
4. Two cells with the same e.m.f. E and different internal resistances r<sub>1</sub> and r<sub>2</sub> are connected in series to an external resistance R. The value of R so that the potential difference across the first cell be zero is
(A) √r1r2 (B) r1+r2 (C) r1−r2 (D) r1+r22
5. Current through ABC and A'B'C' is I. What is the magnetic field at P? BP = PB' = r (Here C'B' PBC are collinear)
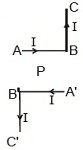
(A) B=14π2Ir (B) B=μ∘4π(2Ir) (C) B=μ∘4π(Ir) (D) Zero
6. The magnetic field at the point of intersection of diagonals of a square wire loop of side L carrying a current I is
(A) μ∘IπL (B) 2μ∘IπL (C) √2μ∘IπL (D) 2√2μ∘IπL
7. In an inelastic collision an electron excites a hydrogen atom from its ground state to a M-shell state. A second electron collides instantaneously with the excited hydrogen atom in the M-State and ionizes it. At least how much energy the second electron transfers to the atom in the M-state ?
(A) +3.4 eV (B) +1.51 eV (C) –3.4 eV (D) –1.51 eV
8. A radioactive nucleus of mass number A, initially at rest, emits an α-particle with a speed v . The recoil speed of the daughter nucleus will be
(A) 2vA−4 (B) 2vA+4 (C) 4vA−4 (D) 4vA+4
9. In the nuclear reaction 147N+X→146C+11H the X will be
(A) 0−1e (B) 11H (C) 21H (D) 10n
10. Which type of Gate the following truth table represents ?
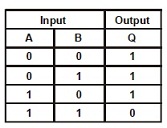
(A) NOT (B) AND (C) OR (D) NAND
11. Given →A=2ˆi+3ˆj and →B=ˆi+ˆj. The component of vector →A along vector →B is
(A) 1√2 (B) 3√2 (C) 5√2 (D) 7√2
12. A cubical vessel of height 1 m is full of water. What is the amount of work done in pumping water out of the vessel ? (Take g = 10 ms<sup>–2</sup>)
(A) 1250 J (B) 5000 J (C) 1000 J (D) 2500 J
13. A stone of relative density K is released from rest on the surface of a lake. If viscous effects are ignored, the stone sinks in water with an acceleration of
(A) g(1 – K) (B) g(1 + K) (C) g(1−1K) (D) g(1+1K)
14. If a person can throw a stone to maximum height of h metre vertically, then the maximum distance through which it can be thrown horizontally by the same person is
(A) h2 (B) h (C) 2h (D) 3h
15. A body of mass 6 kg is acted upon by a force which causes a displacement in it given by x=t24 metre where t is the time in second. The work done by the force in 2 seconds is
(A) 12 J (B) 9J (C) 6 J (D) 3 J
16. A box is moved along a straight line by a machine delivering constant power. The distance moved by the body in time t is proportional to
(A) t12 (B) t34 (C) t32 (D) t2
17. A particle is moving with a constant speed v in a circle. What is the magnitude of average velocity after half rotation ?
(A) 2 v (B) 2vπ (C) v2 (D) v2π
18. A cricket ball of mass 0.25 kg with speed 10 m/s collides with a bat and returns with same speed within 0.01 S. The force acted on bat is
(A) 25 N (B) 50 N (C) 250 N (D) 500 N
19. If the Earth were to suddenly contract to 1nth of its present radius without any change in its mass, the duration of the new day will be nearly
(A) 24/n hr. (B) 24 n hr. (C) 24/n<sup>2</sup> hr. (D) 24 n<sup>2</sup> hr.
20. If g is the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth, the gain in potential energy of an object of mass m raised from the earth’s surface to a height equal to the radius R of the earth is
(A) mgR4 (B) mgR2 (C) mgR (D) 2mgR
21. A material has Poisson’s ratio 0.50. If a uniform rod of it suffers a longitudinal strain of 2 × 10<sup>-3</sup>, then the percentage change in volume is
(A) 0.6 (B) 0.4 (C) 0.2 (D) zero
22. Two identical springs are connected to mass m as shown (k = spring constant). If the period of the configuration in (a) is 2S, the period of the configuration (b) is
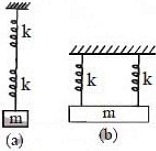
(A) √2S (B) 1S (C) 1√2S (D) 2√2S
23. An object weighs m<sub>1</sub> in a liquid of density d<sub>1</sub> and that in liquid of density d<sub>2</sub> is m<sub>2</sub>. The density d of the object is
(A) d=m2d2−m1d1m2−m1 (B) d=m1d1−m2d2m2−m1 (C) d=m2d1−m1d2m1−m2 (D) d=m1d2−m2d1m1−m2
24. A body floats in water with 40% of its volume outside water. When the same body floats in an oil, 60% of its volume remains outside oil. The relative density of oil is
(A) 0.9 (B) 1.0 (C) 1.2 (D) 1.5
25. Two soap bubbles of radii x and y coalesce to constitute a bubble of radius z. Then z is requal to
(A) √x2+y2 (B) √x+y (C) x+y (D) x+y2
26. A particle of mass m is located in a one dimensional potential field where potential energy is given by : V(x) = A(1 – cos px), where A and p are constants. The period of small oscillations of the particle is
(A) 2π√m(Ap) (B) 2π√m(Ap2) (C) 2π√mA (D) 12π√Apm
27. The period of oscillation of a simple pendulum of length l suspended from the roof of a vehicle, which moves without friction down an inclined plane of inclination α, is given by
(A) 2π√1gcosα (B) 2π√1gsinα (C) 2π√1g (D) 2π√1gtanα
28. In Young’s double slit experiment the two slits are d distance apart. Interference pattern is observed on a screen at a distance D from the slits. A dark fringe is observed on the screen directly opposite to one of the slits. The wavelength of light is
(A) D22d (B) d22D (C) D2d (D) d2D
29. A plane progressive wave is given by y = 2 cos 6.284 (330 t – x). What is period of the wave ?
(A) 1330S (B) 2π×330S (C)(2π×330)−1S (D) 6.284330S
30. The displacement of a particle in S.H.M. varies according to the relation x=4(cosπt+sinπt). The amplitude of the particle is
(A) – 4 (B) 4 (C) 4√2 (D) 8
31. Two temperature scales A and B are related by A−42110=B−72220. At which temperature two scales have the same reading ?
(A) -42° (B) -72° (C) +12° (D) -40°
32. An ideal gas is compressed isothermally until its pressure is doubled and then allowed to expand adiabatically to regain its original volume (γ=1.4 and 2−14=0.38). The ratio of the final to initial pressure is
(A) 0.76 : 1 (B) 1 : 1 (C) 0.66 : 1 (D) 0.86 : 1
33. Air inside a closed container is saturated with water vapour. The air pressure is p and the saturated vapour pressure of water is ˉp . If the mixture is compressed to one half of its volume by maintaining temperature constant, the pressure becomes
(A) 2(p+ˉp) (B) 2p+ˉp (C) (p+ˉp)/2 (D) p+2ˉp
34. 1.56 × 10<sup>5</sup> J of heat is conducted through a 2 m<sup>2</sup> wall of 12 cm thick in one hour. Temperature difference between the two sides of the wall is 20°C. The thermal conductivity of the material of the wall is (in W m<sup>-1</sup> K<sup>-1</sup>)
(A) 0.11 (B) 0.13 (C) 0.15 (D) 1.2
35. A diver at a depth of 12 m in water (μ=43) sees the sky in a cone of semivertical angle :
(A) sin−1(43) (B) tan−1(43) (C) sin−1(34) (D) 90°
36. Two thin lenses of focal lengths 20 cm and 25 cm are placed in cotact. The effective power of the combination is
(A) 9D (B) 2D (C) 3D (D) 7D
37. A convex lens of focal length 30 cm produces 5 times magnified real image of an object. What is the object distance ?
(A) 36 cm (B) 25 cm (C) 30 cm (D) 150 cm
38. If the focal length of the eye piece of a telescope is doubled, its magnifying power (m) will be
(A) 2 m (B) 3 m (C) m2 (D) 4 m
39. A plano-concave lens is made of glass of refractive index 1.5 and the radius of curvature of its curved face is 100 cm. What is the power of the lens ?
(A) +0.5 D (B) –0.5 D (C) –2 D (D) +2 D
40. Four charges equal to –Q are placed at the four corners of a square and a charge q is at its centre. If the system is in equilibrium, the value of q is
(A) −Q4(1+2√2) (B) Q4(1+2√2) (C) −Q2(1+2√2) (D) Q2(1+2√2)
41. Two aromatic compounds having formula C<sub>7</sub>H<sub>8</sub>O which are easily identifiable by FeCl<sub>3</sub> solution test (violet colouration) are
(A) o_- cresol and benzyl alcohol (B) m_-cresol and p-cresol
(C) o_- cresol and p-cresol (D) methyl phenyl ether and benzyl alcohol
42. The ease of dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halide with alcoholic KOH is
(A) 3°< 2°<1° (B) 3°> 2°> 1° (C) 3°< 2°>1° (D) 3°> 2°<1°
43. The ease of Nitration of the following three hydrocarbons follows the order
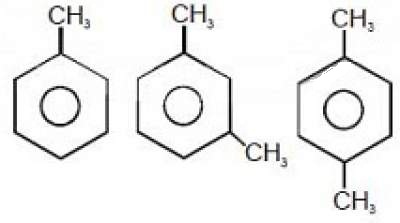
(A) II = III ≈ I (B) II > III > I (C) III > II > I (D) I = III > II
44. The correct order of decreasing acidity of nitrophenols will be
(A) m-Nitrophenol > p-Nitrophenol > o-Nitrophenol (B) o-Nitrophenol > m- Nitrophenol > p-Nitrophenol
(C) p-Nitrophenol > m- Nitrophenol > o-Nitrophenol (D) p-Nitrophenol > o-nitrophenol > m-Nitrophenol
45. Among the alkenes which one produces tertiary butyl alcohol on acid hydration
(A) CH<sub>3</sub> – CH<sub>2</sub> – CH = CH<sub>2</sub> (B) CH<sub>3</sub> – CH = CH – CH<sub>3</sub> (C) (CH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>C = CH<sub>2</sub> (D) CH<sub>3</sub> – CH = CH<sub>2</sub>
46. Which of the following compounds has maximum volatility ?
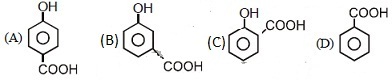
Ans: (C)
47. Which one of the following will show optical isomerism ?
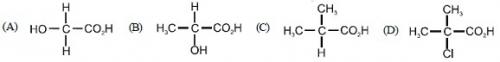
Ans: (B)
48. The pH of an aqueous solution of CH<sub>3</sub>COONa of concentration C(M) is given by
(A) 7−12pKa−12logC (B) 12pKa+12pKb+12logC
(C) 12pKw−12pKb−12logC (D) 12pKw+12pKa+12logC
49. The standard reduction potential E° for half reations are
Zn = Zn<sup>+2</sup> + Ze E°= +0.76 V
Fe = Fe<sup>+2</sup> + Ze E°= + 0.41 V
The EMF of the cell reaction Fe<sup>+2</sup> + Zn = Zn<sup>+2</sup> + Fe is
(A) -0.35 V (B) +0.35 (C) +1.17 V (D) – 1.17 V
50. If the equilibrium constants of the following equilibria SO2+12O2⇌SO3 and 2SO3⇌2SO2+O2 are given by K<sub>1</sub> and K<sub>2</sub> respectively, which of the following relations is correct
(A) K2=(1K1)2 (B) K1=(1K2)3 (C) K2=(1K1) (D) K2=(K1)2
51. The energy of an electron in first Bohr orbit of H – atom is – 13.6 eV. The possible energy value of electron in the excited state of Li<sup>2+</sup> is
(A) – 122.4 eV (B) 30.6 eV (C) – 30.6 eV (D) 13.6 eV
52. The amount of the heat released when 20 ml 0.5 M NaOH is mixed with 100 ml 0.1 M HCl is x kJ. The heat of neutralization is
(A) – 100 x kJ/mol (B) – 50 x kJ/mol (C) + 100 x kJ/mol (D) +50 x kJ/mol
53. Which one of the following has the lowest ionization energy ?
(A) 1s<sup>2</sup>2s<sup>2</sup>2p<sup>6</sup> (B) 1s<sup>2</sup>2s<sup>2</sup>2p<sup>6</sup>3s<sup>1</sup> (C) 1s<sup>2</sup>2s<sup>2</sup>2p<sup>5</sup> (D) 1s<sup>2</sup>2s<sup>2</sup>2p<sup>3</sup>
54. The ozone layer forms naturally by
(A) the interaction of CFC with oxygen (B) the interaction of UV radiation with oxygen
(C) the interaction of IR radiation with oxygen (D) the interaction of oxygen and water vapour.
55. 2 gm of metal carbonate is neutralized completely by 100 ml of 0.1 (N) HCl. The equivalent weight of metal carbonate is
(A) 50 (B) 100 (C) 150 (D) 200
56. Which one of the following is not true at room temperature and pressure
(A) P<sub>4</sub>O<sub>10</sub> is a white solid (B) SO<sub>2</sub> is a coloureless gas
(C) SO<sub>3</sub> is a colourless gas (D) NO<sub>2</sub> is a brown gas
57. An electric current is passed through an aqueous solution of a mixture of alanine (isoelectric point 6.0) glutamic acid (3.2) and arginine (10.7) buffered at pH 6. What is the fate of the three acids ?
(A) Glutamic acid migrates to anode at pH 6. Arginine is present as a cation and migrates to the cathode. Alanine in a dipolar ion remains uniformly distributed in solution.
(B) Glutamic acid migrates to cathode and others remain uniformly distributed in solution.
(C) All three remain uniformly distributed in solution.
(D) All three move to cathode
58. The representation of the ground state electronic configuration of He by box – diagram as ![]() is wrong because it violates
is wrong because it violates
(A) Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle (B) Bohr’s Quantization Theory of Angular Momenta
(C) Pauli Exclusion Principle (D) Hund’s Rule
59. The electronic transitions from n = 2 to n = 1 will produce shortest wavelength in (where n = principal quantum state)
(A) Li<sup>+2</sup> (B) He<sup>+</sup> (C) H (D) H<sup>+</sup>
60. In the following electron – dot structure, calculate the formal charge from left to right nitrogen atom; N\limits_{..}^{..}=N = N\limits_{..}^{..}
(A) – 1, –1, + 1 (B) – 1, +1, – 1 (C) + 1, –1, – 1 (D) + 1, – 1, + 1
61. If the molecular wt. of Na<sub>2</sub>S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> and I<sub>2</sub> are M<sub>1</sub> and M<sub>2</sub> respectively, then what will be the equivalent wt. of Na<sub>2</sub>S<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> and I<sub>2</sub> in the following reaction ?
2S2O2−3+I2→S4O2−6+2I−
(A) M<sub>1</sub>, M<sub>2</sub> (B) M<sub>1</sub>, M<sub>2</sub>/2 (C) 2M<sub>1</sub>, M<sub>2</sub> (D) M<sub>1</sub>, 2M<sub>2</sub>
62. A radioactive atom XYM emits two α particles and one ß particle successively. The number of neutrons in the nucleus of the product will be
(A) X – 4 – Y (B) X – Y – 5 (C) X – Y – 3 (D) X – Y – 6
63. An element belongs to Group 15 and third period of the periodic table. Its electonic configuration will be
(A) 1s<sup>2</sup>2s<sup>2</sup>2p<sup>3</sup> (B) 1s<sup>2</sup>2s<sup>2</sup>2p<sup>4</sup> (C) 1s<sup>2</sup>2s<sup>2</sup>2p<sup>6</sup>3s<sup>2</sup>3p<sup>3</sup> (D) 1s<sup>2</sup>2s<sup>2</sup>2p<sup>6</sup>3s<sup>2</sup>3p<sup>2</sup>
64. Which one of the following is paramagnetic ?
(A) N<sub>2</sub> (B) NO (C) CO (D) O<sub>3</sub>
65. Platinum, Palladium and Iridium are called noble metals because
(A) Alfred Nobel discovered them (B) They are shining lustrous and pleasing to look at
(C) They are found in native state (D) They are inert towards many common reagents.
66. Which one is not a constituent of nucleic acid ?
(A) Uracil (B) Guanidine (C) Phosphoric acid (D) Ribose sugar
67. The sp<sup>3</sup>d<sup>2</sup> hybridization of central atom of a molecule would lead to
(A) square planar geometry (B) Tetrahedral geometry
(C) Trigonal bipyramidal geometry (D) Octahedral geometry
68. In aqueous solution glucose remains as
(A) Only in open chain form (B) Only in pyranoze form
(C) Only in furanose forms (D) In all three forms in equilibrium
69. Which of the following is used to prepare Cl<sub>2</sub> gas at room temperature from concentrated HCl ?
(A) MnO<sub>2</sub> (B) H<sub>2</sub>S (C) KMnO<sub>4</sub> (D) Cr<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub>
70. NO<sub>2</sub> is not obtained on heating
(A) AgNO<sub>3</sub> (B) KNO<sub>3</sub> (C) Cu(NO<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub> (D) Pb(NO<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>
71. The normality of 30 volume H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> is
(A) 2.678 N (B) 5.336 N (C) 8.034 N (D) 6.685 N
72. Reaction of formaldehyde and ammonia gives
(A) Hexamethylene tetramine (B) Bakelite (C) Urea (D) Triethylene Tetramine
73. A plot of In k against 1T (abscissa) is expected to be a straight line with intercept on ordinate axis equal to
(A) △S∘2.303R (B) △S∘R (C) −△S∘R (D) R×△S∘
74. Which of the following represents the composition of Carnallite mineral ?
(A) K<sub>2</sub>O. Al<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub>. 6SiO<sub>2</sub> (B) KNO<sub>3</sub> (C) K<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4</sub>. MgSO<sub>4</sub>. MgCl<sub>2</sub>.6H<sub>2</sub>O (D) KCl. MgCl<sub>2</sub>.6H<sub>2</sub>O
75. The solubility of Ca<sub>3</sub>(PO<sub>4</sub>)<sub>2</sub> in water is y moles / litre. Its solubility product is
(A) 6y<sup>4</sup> (B) 36y<sup>4</sup> (C) 64y<sup>5</sup> (D) 108y<sup>5</sup>
76. Paracetamol is
(A) Methyl salicylate (B) Phenyl salicylate (C) N-acetyl p-amino phenol (D) Acetyl salicylic acid
77. Anhydrous ferric chloride is prepared by
(A) Dissolving Fe(OH)<sub>3</sub> in concentrated HCl (B) Dissolving Fe(OH)<sub>3</sub> in dilute HCl
(C) Passing dry HCl over heated iron scrap (D) Passing dry Cl<sub>2</sub> gas over heated iron scrap
78. Which one of the following is s-butyl phynylvinyl methane ?
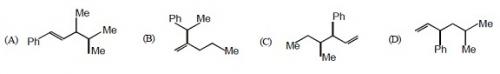
Ans: (C)
79. Hybridization of C<sub>2</sub> and C<sub>3</sub> of H<sub>3</sub>C – CH = C = CH – CH<sub>3</sub> are
(A) Sp, Sp<sup>3</sup> (B) Sp<sup>2</sup>, Sp (C) Sp<sup>2</sup>, Sp<sup>2</sup> (D) Sp, Sp
80. Which of the following compounds is not formed in iodoform reaction of acetone
(A) CH<sub>3</sub>COCH<sub>2</sub>I (B) ICH<sub>2</sub>COCH<sub>2</sub>I (C) CH<sub>3</sub>COCHI<sub>2</sub> (D) CH<sub>3</sub>COCI<sub>3</sub>
***