An electric circuit is a path of connected elements in which electrons can flow from a voltage or current source.
Before going into discussion of network analysis or Circuit is required to know certain definitions.
CIRCUIT ELEMENT:Any individual circuit component (inductor,capacitor,resistor, generator etc) with two terminals, by it can be connected to the other electric components.
BRANCH:A group of circuit elements, usually in series with two terminals.
POTENTIAL SOURCE:
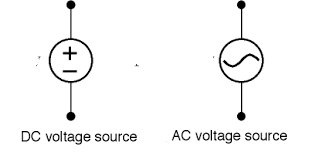 A hypothetical generator which maintains it's value of potential independent of the output current.
A hypothetical generator which maintains it's value of potential independent of the output current.
CURRENT SOURCE:
 A generator which maintains it's output current independent of voltage across it's terminals.
A generator which maintains it's output current independent of voltage across it's terminals.
NETWORK AND CIRCUIT: An electric network is any possible interconnection of electric elements or branches. An electric is closed energized network. A network is not necessarily a circuit; e.g. T-network.
LUMPED NETWORK: A network in which physically separate resistors,capacitors and inductors can be represented.
DISTRIBUTED NETWORK:One in which resistors,capacitors and inductors cannot be electrically separated and individually isolated as separate elements.A transmission line is such a network.
PASSIVE NETWORK: A network containing circuit elements without any energy sources.
ACTIVE NETWORK:A network containing energy sources together with circuit elements.
LINEAR ELEMENT:A circuit element is linear if the relation between current and voltage involves a constant coefficient.
e.g. v=ir
A linear network is one in which the principle of superposition holds.Otherwise the network is called non-linear.
MESS AND LOOP:A set of branches forming a closed path, with the omission of any branch making the path open. Mesh must not have any other circuit inside it. Loop may have other loops or meshes inside.
NODE OR JUNCTION:A terminal of any branch of network common to two or more branches known as a node. Voltage of any node with respect to ground is the node voltage or nodal voltage. Voltage between any pair of nodes is the node pair voltage.
VECTOR AND PHASOR:Vector is a quantity having both magnitude and direction and it is multidimensional. Phasor is a two dimensional vector used in electrical technology which relates to voltage and current.