WEST BENGAL JOINT ENTRANCE EXAM ,2009
PHYSICS AND CHEMISTRY
1. One Kg of copper is drawn into a wire of 1mm diameter and a wire of 2 mm diameter. The resistance of the twowires will be in the ratio
(A) 2 : 1 (B) 1 : 2 (C) 16 : 1 (D) 4 : 1
2. An electrical cable having a resistance of 0.2 Ω delivers 10kw at 200V D.C. to a factory. What is the efficiency of transmission ?
(A) 65% (B) 75% (C) 85% (D) 95%
3. A wire of resistance 5 Ω is drawn out so that its new length is 3 times its original length. What is the reistance of the new wire ?
(A) 45 Ω (B) 15 Ω (C) 5/3 Ω (D) 5 Ω
4. Two identical cells each of emf E and internal resistance r are connected in parallel with an external resistance R. To get maximum power developed across R, the value of R is
(A) R = r/2 (B) R = r (C) R = r/3 (D) R = 2r
5. To write the decimal number 37 in binary, how many binary digits are required ?
(A) 5 (B) 6 (C) 7 (D) 4
6. A junction diode has a resistance of 25 Ω when forward biased and 2500 Ω when reverse biased. The current in the diode, for the arrangement shown will be
![]()
(A) 115A (B) 17A (C) 125A (D) 1180A
7. If the electron in a hydrogen atom jumps from an orbit with level n<sub>1</sub> = 2 to an orbit with level n<sub>2</sub> = 1 the emitted radiation has a wavelength given by
(A) λ = 5/3R (B) λ = 4/3 R (C) λ = R/4 (D) λ = 3R/4
8. What is the particle x in the following nuclear reaction :
94Be+42He→126C+x
(A) electron (B) proton (C) Photon (D) Neutron
9. An alternating current of rms value 10 A is passed through a 12 Ω resistor. The maximum potential difference across the resistor is
(A) 20 V (B) 90 V (C) 1969.68 V (D) none
10. Which of the following relation represent Biot-Savart’s law ?
(A) dˉB=μ04πˉdl×ˉrr (B) dˉB=μ04πˉdl׈rr3
(C) dˉB=μ04πˉdl×ˉrr3 (D) dˉB=μ04πˉdl×ˉrr4
11. →A and →B are two vectors given by →A=2ˆi+3ˆj and →B=ˆi+ˆj . The magnitude of the component of →A along →B is
(A) 5√2 (B) 3√2 (C) 7√2 (D) 1√2
12. Given →C=→A×→B and →D=→B×→A . What is the angle between →C and →D ?
(A) 30° (B) 60° (C) 90° (D) 180°
13. The acceleration ‘a’ (in ms<sup>–2</sup>) of a body, starting from rest varies with time t (in s) following the equation a = 3t + 4 The velocity of the body at time t = 2s will be
(A) 10 ms<sup>–1</sup> (B) 18 ms<sup>–1</sup> (C) 14 ms<sup>–1</sup> (D) 26 ms<sup>–1</sup>
14. Figure below shows the distance-time graph of the motion of a car. If follows from the graph that the car is
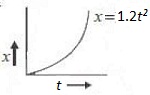
(A) at rest (B) in uniform motion (C) in non-uniform acceleration (D) uniformly accelerated
15. Two particles have masses m & 4m and their kinetic energies are in the ratio 2: 1. What is the ratio of their linear momenta ?
(A) 1√2 (B) 12 (C) 14 (D) 116
16. The force F acting on a particle moving in a straight line is shown below. What is the work done by the force on the particle in the 1<sup>st</sup> meter of the trajectory ?
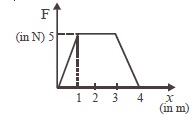
(A) 5 J (B) 10 J (C) 15 J (D) 2.5 J
17. If the kinetic energy of a body changes by 20% then its momentum would change by –
(A) 20% (B) 24% (C) 40% (D) 44%
Ans : (No answer matching)
18. A bullet is fired with a velocity u making an angle of 60° with the horizontal plane. The horizontal component o the velocity of the bullet when it reaches the maximum height is
(A) u (B) 0 (C) √3u2 (D) u2
19. A particle is projected at 60° to the horizontal with a kinetic energy K. The kinetic energy at the highest point is
(A) K (B) zero (C) K4 (D) K2
20. The poisson’s ratio of a material is 0.5. If a force is applied to a wire of this material, there is a decrease in the cross-sectional area by 4%. The percentage increase in the length is :
(A) 1 % (B) 2% (C) 2.5% (D) 4%
21. Two spheres of equal masses but radii r<sub>1</sub> and r<sub>2</sub> are allowed to fall in a liquid of infinite column. The ratio of their terminal velocities is
(A) 1 (B) r<sub>1</sub> : r<sub>2</sub> (C) r<sub>2</sub> : r<sub>1</sub> (D) √r<sub>1</sub> : √r<sub>2</sub>
Ans : (Data incomplete)
22. Two massless springs of force constants K<sub>1</sub> and K<sub>2</sub> are joined end to end. The resultant force constant K of the system is
(A) K=K1+K2K1K2 (B) K=K1−K2K1K2 (C) K=K1K2K1+K2 (D) K=K1K2K1−K2
23. A spring of force constant k is cut into two equal halves. The force constant of each half is
(A) k√2 (B) k (C) k2 (D) 2k
24. Two rods of equal length and diameter have thermal conductivities 3 and 4 units respectively. If they are joined inseries, the thermal conductivity of the combination would be
(A) 3.43 (B) 3.5 (C) 3.4 (D) 3.34
25. 19 g of water at 30°C and 5 g of ice at –20°C are mixed together in a calorimeter. What is the final temperature of the mixture ? Given specific heat of ice = 0.5 cal g<sup>–1</sup>(°C)<sup>–1</sup> and latent heat of fusion of ice = 80 cal g<sup>–1</sup>
(A) 0°C (B) – 5°C (C) 5°C (D) 10°C
26. It is difficult to cook rice in an open vessel by boiling it at high altitudes because of
(A) low boiling point and high pressure (B) high boiling point and low pressure
(C) low boiling point and low pressure (D) high boiling point and high pressure
27. The height of a waterfall is 50 m. If g = 9.8 ms<sup>–2</sup> the difference between the temperature at the top and the bottom of the waterfall is:
(A) 1.17°C (B) 2.17°C (C) 0.117°C (D) 1.43°C
28. The distance between an object and a divergent lens is m times the focal length of the lens. The linear magnification produced by the lens is
(A) m (B) 1m (C) m + 1 (D) 1m+1
29. A 2.0 cm object is placed 15 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. What is the size and nature ofthe image ?
(A) 4 cm. real (B) 4 cm, virtual (C) 1.0 cm, real (D) None
30. A beam of monochromatic blue light of wavelength 4200 Å in air travels in water of refractive index 4/3. Its wavelength in water will be :
(A) 4200 Å (B) 5800 Å (C) 4150 Å (D) 3150 Å
31. Two identical light waves, propagating in the same direction, have a phase difference δ. After they superpose the intensity of the resulting wave will be proportional to
(A) cos δ (B) cos (δ/2) (C) cos²(δ/2) (D) cos²δ
32. The equation of state for n moles of an ideal gas is PV = nRT, where R is a constant. The SI unit for R is
(A) JK<sup>–1</sup> per molecule (B) JK<sup>–1</sup> mol<sup>–1</sup> (C) J Kg<sup>–1</sup> K<sup>–1</sup> (D) JK<sup>–1</sup> g<sup>–1</sup>
33. At a certain place, the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field is √3 times the vertical component. Theangle of dip at that place is
(A) 30° (B) 60° (C) 45° (D) 90°
34. The number of electron in 2 coulomb of charge is
(A) 5 × 10<sup>29</sup> (B) 12.5 × 10<sup>18</sup> (C) 1.6 × 10<sup>19</sup> (D) 9 × 10<sup>11</sup>
35. The current flowing through a wire depends on time as I = 3t² + 2t + 5. The charge flowing through the cross section of the wire in time from t = 0 to t = 2 sec. is
(A) 22 C (B) 20 C (C) 18 C (D) 5 C
36. If the charge on a capacitor is increased by 2 coulomb, the energy stored in it increases by 21%. The original charge on the capacitor is
(A) 10 C (B) 20 C (C) 30 C (D) 40 C
37. The work done in carrying a charge Q once around a circle of radius r about a charge q at the centre is
(A) qQ4πε0r (B) qQ4πε01πr (C) qQ4πε0(12πr) (D) 0
38. Four capacitors of equal capacitance have an equivalent capacitance C<sub>1</sub> when connected in seriesand an equivalent capacitance C<sub>2</sub> when connected in parallel. The ratio C1C2 is:
(A) 1/4 (B) 1/16 (C) 1/8 (D) 1/12
39. Magnetic field intensity H at the centre of a circular loop of radius r carrying current I e.m.u is
(A) r/I oersted (B) 2πI/r oersted (C) I/2πr oersted (D) 2πr/I oersted
40. Which of the following materials is the best conductor of electricity ?
(A) Platinum (B) Gold (C) Silicon (D) Copper
41. Which statement is incorrect
(A) Phenol is a weak acid (B) Phenol is an aromatic compound
(C) Phenol liberates CO<sub>2</sub> from Na<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub> soln (D) Phenol is soluble inNaOH
42. In which of the following reactions new carbon-carbon bond is not formed :
(A) Cannizaro reaction (B) Wurtz reaction (C) Aldol condensation (D) Friedel-Craft reaction
43. A compound is formed by substitution of two chlorine for two hydrogens in propane. The number of possible isomeric compounds is
(A) 4 (B) 3 (C) 5 (D) 2
44. Which one of the following is called a carbylamine ?
(A) R CN (B) R CONH<sub>2</sub> (C) R–CH=NH (D) R NC
45. For making distinction between 2-pentanone and 3-pentanone the reagent to be employed is
(A) K<sub>2</sub>Cr<sub>2</sub>O<sub>7</sub>/H<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4</sub> (B) Zn-Hg/HCl (C)SeO<sub>2</sub> (D) Iodine/NaOH
46. Which one of the following formulae does not represent an organic compound ?
(A) C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>10</sub>O<sub>4</sub> (B) C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>8</sub>O<sub>4</sub> (C) C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>7</sub>CIO<sub>4</sub> (D) C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>9</sub>O<sub>4</sub>
47. The catalyst used for olefin polymerization is
(A) Ziegler-Natta Catalyst (B) Wilkinson Catalyst (C) Raney nickel catalyst (D) Merrifield resin
48. The oxidant which is used as an antiseptic is :
(A) KBrO<sub>3</sub> (B) KMnO<sub>4</sub> (C) CrO<sub>3</sub> (D) KNO<sub>3</sub>
49. Which of the following contributes to the double helical structure of DNA
(A) hydrogen bond (B) covalent bond (C) disulphide bond (D) van-der Waal’s force
50. The monomer used to produce orlon is
(A) CH<sub>2</sub>=CHF (B) CH<sub>2</sub>=C Cl<sub>2</sub> (C) CH<sub>2</sub>=CH Cl (D)CH<sub>2</sub>=CH-CN
51. 1 mole of photon, each of frequency 2500 S<sup>-1</sup>, would have approximately a total energy of :
(A) 1 erg (B) 1 Joule (C) 1 eV (D) 1 MeV
52. If n<sub>t</sub> number of radioatoms are present at time t, the following expression will be a constant :
(A) n<sub>t</sub>/t (B) In n<sub>t</sub>/t (C) d In n<sub>t</sub>/dt (D) t.n<sub>t</sub>
53. The following graph shows how T<sub>1/2</sub> (half-life) of a reactant R changes with the initial reactant concentration a<sub>0</sub>.
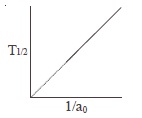
The order of the reaction will be :
(A) 0 (B) 1 (C) 2 (D) 3
54. The second law of thermodynamics says that in a cyclic process :
(A) work cannot be converted into heat (B) heat cannot be converted into work
(C) work cannot be completely converted into heat (D) heat cannot be completely converted into work
55. The equilibrium constant (K) of a reaction may be written as :
(A) K = e<sup>−ΔG/ RT</sup> (B) K = e<sup>−ΔG°/ RT</sup> (C) K = e<sup>−ΔH/ RT</sup> (D) K = e<sup>−ΔH°/ RT</sup>
56. For the reaction SO2+12O2=SO3, if we write Kp=Kc(RT)x, then x becomes
(A) –1 (B) −12 (C) 12 (D) 1
57. If it is assumed that 23592U decays only by emitting α and β particles, the possible product of the decay is :
(A) 22589Ac (B) 22789Ac (C) 23089Ac (D) 23189Ac
58. The time taken for 10% completion of a first order reactin is 20 mins. Then, for 19% completion, the reaction will take
(A) 40 mins (B) 60 mins (C) 30 mins (D) 50 mins
59. Which of the following will decrease the pH of a 50 ml solution of 0.01 M HCl ?
(A) addition of 5 ml of 1 M HCl (B) addition of 50 ml of 0.01 M HCl
(C) addition of 50 ml of 0.002 M HCl (D) addition of Mg
60. Equal volumes of molar hydrochloric acid and sulphuric acid are neutralised by dilute NaOH solution and x kcal and y kcal of heat are liberated respectively. Which of the following is true ?
(A) x=y (B) x=y2 (C) x=2y (D) none of the above
61. Hybridisation of central atom in NF<sub>3</sub> is
(A) sp<sup>3</sup> (B) sp (C) sp² (D) dsp²
62. Of the following compounds the most acidic is
(A) As<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> (B) P<sub>2</sub>O<sub>5</sub> (C) Sb<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> (D) Bi<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub>
63. The half-life of a radioactive element is 10 hours. How much will be left after 4 hours in 1 g atom sample ?
(A) 45.6 × 10<sup>23</sup> atoms (B) 4.56 × 10<sup>23</sup> atoms (C) 4.56 × 10<sup>21</sup> atoms (D) 4.56× 10<sup>20</sup> atoms
64. For the Paschen series the values of n<sub>1</sub> and n<sub>2</sub> in the expression △E=Rhc(1n21−1n22) are
(A) n<sub>1</sub>=1, n<sub>2</sub>=2, 3, 4........ (B) n<sub>1</sub>=2, n<sub>2</sub>=3, 4, 5........ (C)n<sub>1</sub>=3, n<sub>2</sub>=4, 5, 6........ (D) n<sub>1</sub>=4, n<sub>2</sub>=5, 6, 7.......
65. Under which of the following condition is the relation ΔH = ΔE + PΔV valid for a closed system ?
(A) Constant Pressure (B) Constant temperature
(C) Constant temperature and pressure (D) Constant temperature, pressure and composition
66. An organic compound made of C, H and N contains 20% nitrogen. Its molecular weight is :
(A) 70 (B) 140 (C) 100 (D) 65
67. In Cu-ammonia complex, the state of hybridization of Cu<sup>+2</sub> is
(A) sp<sup>3</sup> (B) d<sup>3</sup>s (C) sp²f (D) dsp²
68. The reaction that takes place when Cl<sub>2</sub> gas is passed through conc. NaOH solution is :
(A) Oxidation (B) Reduction (C) Displacement (D) Disproportionation
69. “Electron” is an alloy of
(A) Mg and Zn (B) Fe and Mg (C) Ni and Zn (D) Al and Zn
70. Blackened oil painting can be restored into original form by the action of :
(A) Chlorine (B) BaO<sub>2</sub> (C) H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> (D) MnO<sub>2</sub>
71. Of the following acids the one which has the capability to form complex compound and also possesses oxidizingand reducing properties is :
(A) HNO<sub>3</sub> (B) HNO<sub>2</sub> (C) HCOOH (D) HCN
72. Atoms in a P<sub>4</sub> molecule of white phosphorus are arranged regularly in the following way :
(A) at the corners of a cube (B) at the corners of a octahedron
(C) at the corners of a tetrahedron (D) at the centre and corners of a tetrahedron
73. Which of the following statements is not correct
(A) Silicon is extensively used as a semiconductor (B) Carborundum is SiC
(C) Silicon occurs in free state in nature (D) Mica contains the element silicon
74. In aluminium extraction by the Bayer process, alumina is extracted from bauxite by sodium hydroxide at high temperature and pressures :
Al2O3(s)+2OH−(aq)→2Al2O−2(aq)+H2O(1)
Solid impurities such as Fe<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> and SiO<sub>2</sub> are removed and then Al(OH)−4 is reprecipitated :
2Al(OH)−4→Al2O3.3H2O(s)+2OH−(aq) . In the industrial world :
(A) Carbon dioxide is added to precipitate the alumina
(B) Temperature and pressure are dropped and the supersaturated solution seeded
(C) Both (A) and (B) are practised
(D) The water is evaporated
75. The addition of HBr to 2-pentene gives
(A) 2-bromopentane only (B) 3-bromopentane only
(C) 2-bromopentane and 3-bromopentane (D) 1-bromopentane and 3-bromopentane
76. Ethelene can be separated from acetylene by passing the mixture through :
(A) fuming H<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4</sub> (B) pyrogallol (C) ammoniacal Cu<sub>2</sub>Cl<sub>2</sub> (D) Charcoal powder
77. Reaction of R OH with R' MgX produces :
(A) RH (B) R′ H (C) R - R (D) R′ - R′
78. In the compound HC ≡ C – CH = CH<sub>2</sub> the hybridization of C – 2 and C – 3 carbons are respectively :
(A) sp<sup>3</sup> & sp<sup>3</sup> (B) sp² & sp<sup>3</sup> (C) sp² & sp (D) sp<sup>3</sup> & sp
79. The two structures written below represent
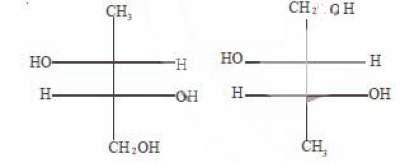
(A) pair of diastereomers (B) pair of enantiomers (C) same molecule (D) both are optically inactive
80. Which of the following carbocations will be most stable ?
(A) P{h_3} C\limits^ + (B) C{H_3} - C\limits^ + {H_3} (C) {(C{H_3})_2}C\limits^ + H (D) C{H_2} = CH - C\limits^ + {H_2}
***






