1. Consider three vectors [tex]\vec{A} = \hat{i} + \hat {j} -2\hat{k}[/tex], [tex]\vec{B}=\hat{i}-\hat{j}+\hat{k}[/tex] and [tex]\vec{C}=2\hat{i}-3\hat{j}+4\hat{k}[/tex]. A vector [tex]\vec{X}[/tex] of the form [tex]\alpha\vec{A}+\beta\vec{B}[/tex] ([tex]\alpha[/tex] and [tex]\beta[/tex] are numbers) is perpendicular to [tex]\vec{C}[/tex]. The ratio of [tex]\alpha[/tex] and [tex]\beta[/tex] is
(A) 1 : 1 (B) 2 : 1 (C) -1 : 1 (D) 3 : 1
2. Three capacitors 3 µF, 6 µF and 6 µF are connected in series to a source of 120 V. The potential difference in volts across the 3 µF capacitor will be
(A) 24 (B) 30 (C) 40 (D) 60
3. A galvanometer having internal resistance 10 Ω requires 0.01 A for a full scale deflection. To convert this galvanometer to a voltmeter of full-scale deflection at 120 V, we need to connect a resistance of
(A) 11990 Ω in series (B) 11990 Ω in parallel (C) 12010 Ω in series (D) 12010 Ω in parallel
4. A whistle whose air column is open at both ends has a fundamental frequency of 5100 Hz. If the speed of sound in air is 340 ms-1, the length of the whistle, in cm, is
(A) 5/3 (B) 10/3 (C) 5 (D) 20/3
5. The output Y of the logic circuit given below is
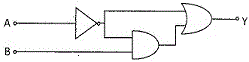
(A) [tex]\bar {A} + B[/tex] (B) [tex]\bar {A}[/tex] (C) [tex] \overline {(\bar A + B)}.\bar A[/tex] (D) [tex]\overline {(\bar A + B)}.A[/tex]
6. One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas is heated at a constant pressure from 0°C to 100°C. Then the change in the internal energy of gas is (Given R = 8.32 Jmol-1K-1)
(A) 0.83 x 10³ J (B) 4.6 x 10³ J (C) 2.08 x 10³ J (D) 1.25 x 10³ J
7. The ionization energy of hydrogen is 13.6 eV. The energy of the photon released when an electron jumps from the first excited state (n = 2) to the ground state of hydrogen atom is
(A) 3.4 eV (B) 4.53 eV (C) 10.2 eV (D) 13.6 eV
8. A parallel plate capacitor is charged and then disconnected from the charging battery. If the plates are now moved farther apart by pulling at them by means of insulating handles, then
(A) the energy stored in the capacitor decreases
(B) the capacitance of the capacitor increases
(C) the charge on the capacitor decreases
(D) the voltage across the capacitor increases
9. When a particle executing SHM oscillates with a frequency ν, then the kinetic energy of the particle
(A) changes periodically with a frequency of ν
(B) changes periodically with a frequency of 2ν
(C) changes periodically with a frequency of ν/2
(D) remains constant
10. In which of the following pairs, the two physical quantities have different dimension ?
(A) Planck's constant and angular momentum
(B) Impulse and linear momentum
(C) Moment of inertia and moment of a force
(D) Energy and torque
11. A cricket ball thrown across a field is at heights h1 and h2 from the point of projection at times [tex]t_1[/tex] and [tex]t_2[/tex] respectively after the throw. The ball is caught by a fielder at the same height as that of projection. The time of flight of the ball in this journey is
(A) [tex]\frac{h_1t_2^2-h_2t_1^2}{h_1t_2-h_2t_1}[/tex] (B) [tex]\frac{h_1t_1^2+h_2t_2^2}{h_2t_1+h_1t_2}[/tex] (C) [tex]\frac{h_1t_2^2+h_2t_1^2}{h_1t_2+h_2t_1}[/tex] (D) [tex]\frac{h_1t_1^2-h_2t_2^2}{h_1t_1-h_2t_2}[/tex]
12. A small metal sphere of radius [tex]a[/tex] is falling with a velocity [tex]v[/tex] through a vertical column of a viscous liquid. If the coefficient of viscosity of the liquid is [tex]\eta[/tex], then the sphere encounters an opposing force of
(A) [tex]6\pi\eta a^2v[/tex] (B) [tex]\frac{6\eta v}{\pi a}[/tex] (C) [tex]6\pi\eta av[/tex] (D) [tex]\frac{\pi\eta v}{6a^3}[/tex]
13. A scientist proposes a new temperature scale in which the ice point is 25 X (X is the new unit of temperature) and the steam point is 305 X. The specific heat capacity of water in this new scale is (in Jkg-1X-1)
(A) 4.2 x 10³ (B) 3.0 x 10³ (C) 1.2 x 10³ (D) 1.5 x 10³
14. One mole of a van Der Waals' gas obeying the equation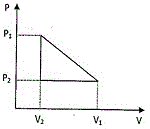
[tex](P+\frac{a}{V^2})(V-b)=RT[/tex]
undergoes the quasi-static cyclic process which is shown in the P-V diagram. The net heat absorbed by the gas in this process is
(A) [tex]\frac{1}{2}(P_1-P_2)(V_1-V_2)[/tex]
(B) [tex]\frac{1}{2}(P_1+P_2)(V_1-V_2)[/tex]
(C) [tex]\frac{1}{2}(P_1+\frac{a}{V_1^2}-P_2-\frac{a}{V_2^2})(V_1-V_2)[/tex]
(D) [tex]\frac{1}{2}(P_1+\frac{a}{V_1^2}+P_2+\frac{a}{V_2^2})(V_1-V_2)[/tex]
15. A wooden block is floating on water kept in a beaker. 40% of the block is above the water surface. Now the beaker is kept inside a lift that starts going upward with acceleration equal to g/2. The block will then
(A) sink
(B) float with 10% above the water surface
(C) float with 40% above the water surface
(D) float with 70% above the water surface
16. A smooth massless string passes over a smooth fixes pulley. Two masses m1 and m2[/tex], (m1 > m2) are tied at the two ends of the string. The masses are allowed to move under gravity starting from rest. The total external force acting on the two masses is
(A) [tex](m_1+m_2)g[/tex] (B) [tex]\frac{{(m_1-m_2)}^2}{m_1+m_2}g[/tex] (C) [tex](m_1 - m_2)g[/tex] (D) [tex]\frac{{(m_1 + m_2)}^2}{m_1 - m_2}g[/tex]
17. To determine the coefficient of friction between a rough surface and a block, the surface is kept inclined at 45° and the block is releases from rest. The block takes a time t in moving a distance d. The rough surface is then replaced by a smooth surface and the same experiment is repeated. The block now takes a time t/2 in moving down the same distance d. The coefficient of friction is
(A) 3/4 (B) 5/4 (C) 1/2 (D) 1/√2
18. A metal rod is fixed rigidly at two ends so as to prevent its thermal expansion. If L, α and γ respectively denote the length of rod, coefficient of linear thermal expansion and Young's modulus of its material, hen for an increase in temperature of the rod by ΔT, the longitudinal stress developed in the road is
(A) inversely proportional to α
(B) inversely proportional to γ
(C) directly proportional to [tex] {\triangle T} \over {\gamma } [/tex]
(D) independent of L
19. A particle is moving uniformly in a circular path of radius r . When it moves through an angular displacement [tex]\theta[/tex], then the magnitude of the corresponding linear displacement will be
(A) [tex]2r \cos (\frac{\theta}{2})[/tex] (B) [tex]2r \cot (\frac{\theta}{2})[/tex] (C) [tex]2r \tan (\frac{\theta}{2})[/tex] (D) [tex]2r \sin (\frac{\theta}{2})[/tex]
20. A uniform rod is suspended horizontally from its mid-point. A piece of metal whose weight is [tex]W[/tex] is suspended at a distance [tex]l[/tex] from the mid-point. Another weight [tex]W_1[/tex] is suspended on the other side at a distance [tex]l_1[/tex] from the mid-point to bring the rod to a horizontal position. When [tex]W[/tex] is completely immersed in water, [tex]W_1[/tex] needs to be kept at a distance [tex]l_2[/tex] from the mid-point to get the rod back into horizontal position. The specific gravity of the metal piece is
(A) [tex]\frac{W}{W_1}[/tex] (B) [tex]\frac{Wl_1}{Wl-W_1l_2}[/tex] (C) [tex]\frac{l_1}{l_1-l_2}[/tex] (D) [tex]\frac{l_1}{l_2}[/tex]
21. A drop of some liquid of volume 0.04 cm³ is placed on the surface of a glass slide. Then another glass slide is placed on it in such a way that the liquid forms a thin layer of ares 20 cm² between the surfaces of the two slides. To separate the slides a force of 16 x 105 dyne has to be applied normal to the surfaces. The surface tension of the liquid is (in dyne-cm-1)
(A) 60 (B) 70 (C) 80 (D) 90
22. An electron in a circular orbit of radius 0.05 nm performs 1016 revolutions per second. The magnetic moment due to this rotation of electron is (in Am²)
(A) 2.16 x 10-23 (B) 3.21 x 10-22 (C) 3.21 x 10-24 (D) 1.26 x 10-23
23. A very small circular loop of radius a is initially (at t = 0) coplanar and concentric with a much larger fixed circular loop of radius b. A constant current I flows in the larger loop. The smaller loop is rotated with a constant angular speed ω about the common diameter. The emf induced in the smaller loop as a function of time t is
(A) [tex]\frac{\pi a^2\mu_0I}{2b}\omega \cos (\omega t)[/tex] (B) [tex]\frac{\pi a^2\mu_0I}{2b}\omega \sin (\omega^2 t^2)[/tex] (C) [tex]\frac{\pi a^2\mu_0I}{2b}\omega \sin (\omega t)[/tex] (D) [tex]\frac{\pi a^2\mu_0I}{2b}\omega \sin^2 (\omega t)[/tex]
24. A luminous object is separated from a screen by distance d. A convex lens is placed between the object and the screen such that it forms a distinct image on the screen. The maximum possible focal length of this convex lens is
(A) 4d (B) 2d (C) d/2 (D) d/4
25. A infinite sheet carrying a uniform surface charge density [tex]\sigma[/tex] lies on the xy-plane. The work done to carry a charge q from the point [tex]\vec{A}=a(\hat{i}+2\hat{j}+3\hat{k})[/tex] to the point [tex]\vec{B}=a(\hat{i}-2\hat{j}+6\hat{k})[/tex] (where a is a constant with the dimension of length and [tex]\epsilon_0[/tex] is the permittivity of free space ) is
(A) [tex]\frac{3\sigma aq}{2\epsilon_0}[/tex] (B) [tex]\frac{2\sigma aq}{\epsilon_0}[/tex] (C) [tex]\frac{5\sigma aq}{2\epsilon_0}[/tex] (D) [tex]\frac{3\sigma aq}{\epsilon_0}[/tex]
26. The intensity of magnetization of a bar magnet is 5.0 x 104 Am-1. The magnetic length and the area of cross section of the magnet are 12 cm and 1 cm² respectively. The magnitude of magnetic moment of this bar magnet is (in SI unit)
(A) 0.6 (B) 1.3 (C) 1.24 (D) 2.4
27. A particle moves with constant acceleration along a straight line starting from rest. The percentage increase in its displacement during the 4th second compared to that in the 3rd second is
(A) 33% (B) 40% (C) 66% (D) 77%
28. A portion of mass m and charge q is moving in a plane with kinetic energy E. If there exists a uniform magnetic field B, perpendicular to the plane of the motion, the proton will move in a circular path of radius
(A) [tex]\frac{2Em}{qB}[/tex] (B) [tex]\frac{\sqrt{2Em}}{qB}[/tex] (C) [tex]\frac{\sqrt{Em}}{2qB}[/tex] (D) [tex]\sqrt{\frac{2Eq}{mB}}[/tex]
29. An artificial satellite moves in a circular orbit around the earth. Total energy of the satellite is given by E. The potential energy of the satellite is
(A) -2E (B) 2E (C) 2E/3 (D) -2E/3
30. In which of the following phenomena, the heat waves travel along straight lines with the speed of light ?
(A) thermal conduction (B) forced convection (C) natural convection (D) thermal radiation
31. If the bandgap between valence band and conduction band in a material is 5.0 eV, then the material is
(A) semiconductor (B) good conductor (C) superconductor (D) insulator
32. A uniform solid spherical ball is rolling down a smooth inclined plane from a height h. The velocity attained by the ball when it reaches the bottom of the inclined plane is v. If the ball is now thrown vertically upwards with the same velocity v, the maximum height to which the ball will rise is
(A) 5h/8 (B) 3h/5 (C) 5h/7 (D) 7h/9
33. Two coherent monochromatic beams of intensities I and 4I respectively are superposed. The maximum and minimum intensities in the resulting pattern are
(A) 5 I and 3 I (B) 9 I and 3 I (C) 4 I and I (D) 9 I and I
34. In the circuit shown assume the diode to be ideal. When [tex]V_i[/tex] increases from 2V to 6V, the change in the current is (in mA)
![]()
(A) zero (B) 20 (C) 80/3 (D) 40
35. If n denotes a positive integer, h the Planck's constant, q the charge and B the magnetic field, then the quantity [tex](\frac{nh}{2\pi qB})[/tex] has the dimension of
(A) area (B) length (C) speed (D) acceleration
36. In a transistor output characteristics commonly used in common emitter configuration, the base current [tex]I_B[/tex], the collector current [tex]I_C[/tex] and the collector-emitter voltage [tex]V_{CE}[/tex] have values of the following orders of magnitude in the active region
(A) [tex]I_B[/tex] and [tex]I_C[/tex] both are in [tex]\mu A[/tex], and [tex]V_{CE}[/tex] in Volts
(B) [tex]I_B[/tex] is in [tex]\mu A[/tex] and [tex]I_C[/tex] is in mA and [tex]V_{CE}[/tex] in Volts
(C) [tex]I_B[/tex] is in mA and [tex]I_C[/tex] is in [tex]\mu A[/tex] and [tex]V_{CE}[/tex] in mV
(D) [tex]I_B[/tex] is in mA and [tex]I_C[/tex] is in mA and [tex]V_{CE}[/tex] in mV
37. The displacement of a particle in a periodic motion is given by [tex]y=4 \cos^2(\frac{t}{2}) \sin (1000t)[/tex]. This displacement may be considered as the result of superposition of [tex]n[/tex] independent harmonic oscillations. Here [tex]n[/tex] is
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
38. Consider a blackbody radiation in a cubical box at absolute temperature T. If the length of each side of the box is doubled and the temperature of the walls of the box and that of the radiation is halved, then the total energy
(A) halves (B) doubles (C) quadruples (D) remains the same
39. Consider two concentric spherical metal shells of the radii [tex]r_1[/tex] and [tex]r_2[/tex], [tex](r_2>r_1)[/tex]. If the outer shell has a charge q and the inner one is grounded, the charge on the inner shell is
(A) [tex]\frac{-r_2}{r_1}q [/tex] (B) zero (C) [tex]\frac{-r_1}{r_2}q[/tex] (D) - q
40. Four cells, each of emf E and internal resistance r, are connected in series across an external resistance R. By mistake one of the cells is connected in reverse. Then the current in the external circuit is
(A) [tex]\frac{2E}{4r+R}[/tex] (B) [tex]\frac{3E}{4r+R}[/tex] (C) [tex]\frac{3E}{3r+R}[/tex] (D) [tex]\frac{2E}{3r+R}[/tex]
41. Same quantity of ice is filled in each of the two metal containers P and Q having the same size, shape and wall thickness but made of different materials. The containers are kept in identical surroundings. The ice in P melts completely in time [tex]t_1[/tex] whereas that in Q takes a time [tex]t_2[/tex]. The ratio of thermal conductivities of the materials of P and Q is
(A) [tex]t_2:t_1[/tex] (B) [tex]t_1:t_2[/tex] (C) [tex]t_1^2:t_2^2[/tex] (D) [tex]t_2^2:t_1^2[/tex]
42. For the radioactive nuclei that undergo either [tex]\alpha[/tex] or [tex]\beta[/tex] decay, which one of the following cannot occur ?
(A) isobar of original nucleus is produced
(B) isotope of original nucleus is produced
(C) nuclei with higher atomic number than that of the original nucleus is produced
(D) nuclei with lower atomic number than that of the original nucleus is produced
43. A car is moving with a speed of 72 km-hour-1 towards a roadside source that emits sound at a frequency of 850 Hz. The car driver listens to the sound while approaching the source and again while moving away from the source after crossing it. If the velocity of sound is 340 ms-1, the difference of the two frequencies, the driver hears is
(A) 50 Hz (B) 85 Hz (C) 100 Hz (D) 150 Hz
44. The energy of gamma [tex](\gamma)[/tex] ray photon is [tex]E_{\gamma}[/tex] and that of an X-ray photon is [tex]E_X[/tex]. If the visible light photon has an energy of [tex]E_V[/tex], then we can say that
(A) [tex]E_X>E_{\gamma}>E_V[/tex] (B) [tex]E_{\gamma}>E_V>E_X[/tex] (C) [tex]E_{\gamma}>E_X>E_V[/tex] (D) [tex]E_X>E_V>E_{\gamma}[/tex]
45. The intermediate image formed by the objective of a compound microscope is
(A) real, inverted and magnified
(B) real, erect and magnified
(C) virtual, erect and magnified
(D) virtual, inverted and magnified
46. A solid uniform sphere resting on a rough horizontal plane is given a horizontal impulse directed through its center so that it starts sliding with an initial velocity [tex]v_0[/tex]. When it finally starts rolling without slipping the speed of its center is
(A) [tex]\frac{2}{7}v_0[/tex] (B) [tex]\frac{3}{7}v_0[/tex] (C) [tex]\frac{5}{7}v_0[/tex] (D) [tex]\frac{6}{7}v_0[/tex]
47. The de Broglie wavelength of an electron is the same as that of a 50 keV X-ray photon. The ratio of the energy of the photon to the kinetic energy of the electron is (the energy equivalent of electron mass is 0.5 MeV)
(A) 1 : 50 (B) 1 : 20 (C) 20 : 1 (D) 50 : 1
48. A glass slab consists of thin uniform layers of progressively decreasing refractive indices RI (see figure) such that the RI of any layer is μ-mΔμ. Here μ and Δμ denote the RI of 0th layer and the difference in RI between any two consecutive layers, respectively. The integer m = 0,1,2,3... denotes the numbers of the successive layers. A ray of light from the 0th layer enters the 1st layer at an angle of incidence of 30°. After undergoing the mth refraction, the ray emerges parallel to the interface. If μ = 1.5 and Δμ = 0.015, the value of m is
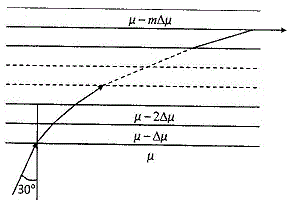
(A) 20 (B) 30 (C) 40 (D) 50
49. A long conducting wire carrying a current I is bent at 120° (see figure). The magnetic field B at a point P on the right bisector of bending angle at a distance d from the bend is ([tex]\mu_0[/tex] is the permeability of free space)
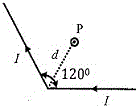
(A) [tex]\frac{3\mu_0I}{2\pi d}[/tex] (B) [tex]\frac{\mu_0I}{2\pi d}[/tex] (C) [tex]\frac{\mu_0I}{\sqrt3\pi d}[/tex] (D) [tex]\frac{\sqrt3\mu_0I}{2\pi d}[/tex]
50. A circuit consists of three batteries of emf [tex]E_1=1 V[/tex], [tex]E_2=2 V[/tex] and [tex]E_3=3 V[/tex] and internal resistances 1Ω, 2Ω and 1Ω respectively which are connected in parallel as shown in the figure. The potential difference between points P and Q is
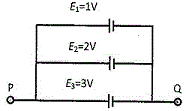
(A) 1.0 V (B) 2.0 V (C) 2.2 V (D) 3.0 V
51. Sound waves are passing through two routes- one in straight path and the other along a semicircular path of radius r, and are again combined into one pipe and superposed as shown in the figure. If the velocity of sound waves in the pipe is v, then frequencies of resultant waves of maximum amplitude will be integral multiples of

(A) [tex]\frac{v}{r(\pi-2)}[/tex] (B) [tex]\frac{v}{r(\pi-1)}[/tex] (C) [tex]\frac{2v}{r(\pi-1)}[/tex] (D) [tex]\frac{v}{r(\pi+1)}[/tex]
52. The determine the composition of a bimetallic alloy, a sample is first weighed in air and then in water. These weights are found to be [tex]w_1[/tex] and [tex]w_2[/tex] respectively. If the densities of the two constituent metals are [tex]\rho_1[/tex] and [tex]\rho_2[/tex] respectively, then the weight of the first metal is in the sample is (where [tex]\rho_w[/tex] is the density of water)
(A) [tex]\frac{\rho_1}{\rho_w(\rho_2-\rho_1)}[w_1(\rho_2-\rho_w)-w_2\rho_2][/tex]
(B) [tex]\frac{\rho_1}{\rho_w(\rho_2+\rho_1)}[w_1(\rho_2-\rho_w)+w_2\rho_2][/tex]
(C) [tex]\frac{\rho_1}{\rho_w(\rho_2-\rho_1)}[w_1(\rho_2+\rho_w)-w_2\rho_1][/tex]
(D) [tex]\frac{\rho_1}{\rho_w(\rho_2-\rho_1)}[w_1(\rho_1-\rho_w)-w_2\rho_1][/tex]
53. A 10 Watt electric heater is used to heat a container filled with 0.5 kg of water. It is found that the temperature of water and the container rises by 3°K in 15 minutes. The container is then emptied, dried and filled with 2 kg of oil. The same heater now rises the temperature of container-oil system by 2°K in 20 minutes. Assuming that there is no heat loss in the process and the specific heat of water as 4200 Jkg-1K-1, the specific heat of oil in the same unit is equal to
(A) 1.50 x 10³ (B) 2.55 x 10³ (C) 3.00 x 10³ (D) 5.10 x 10³
54. An object is placed 30 cm away from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm and a sharp image is formed on a screen. Now a concave lens is placed in contact with the convex lens. The screen now has to be moved by 45 cm to get a sharp image again. The magnitude of focal length of the concave lens is (in cm)
(A) 72 (B) 60 (C) 36 (D) 20
55. Three identical square plates rotate about the axes shown in the figure in such a way that their kinetic energies are equal. Each of the rotation axes passes through the centre of the square. Then the ratio of angular speeds [tex]\omega_1:\omega_2:\omega_3[/tex] is
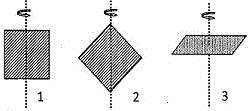
(A) 1 : 1 : 1 (B) √2 : √2 : 1 (C) 1 : √2 : 1 (D) 1 : 2 : √2
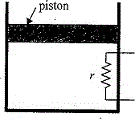
56. A heating element of resistance r is fitted inside an adiabatic cylinder which carries a frictionless piston of mass m and cross-section A as shown in diagram. The cylinder contains one mole of an ideal diatomic gas. The current flows through the element such that the temperature rises with time t as [tex]\Delta T=\alpha t+\frac{1}{2}\beta t^2[/tex] ([tex]\alpha[/tex] and [tex]\beta[/tex] are constants), while pressure remains constant. The atmospheric pressure above the piston is [tex]P_0[/tex]. Then
(A) the rate of increase in internal energy is [tex]\frac{5}{2}R(\alpha+\beta t)[/tex]
(B) the current flowing in the element is [tex]\sqrt{\frac{5}{2r}R(\alpha+\beta t)}[/tex]
(C) the piston moves upwards with constant acceleration
(D) the piston moves upwards with constant speed
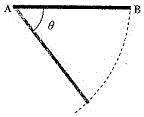
57. A thin rod AB is held horizontally so that it can freely rotate in a vertical plane about the end A as shown in the figure. The potential energy of the rod when it hangs vertically is taken to be zero. The end B of the rod is released from rest from a horizontal position. At the instant the rod makes an angle θ with the horizontal
(A) the speed of end B is proportional to [tex]\sqrt{sin\theta}[/tex]
(B) the potentail energy is proportional to (1 - cos θ)
(C) the angular acceleration is proportional to cos θ
(D) the torque about A remains the same as its initial value
58. Find the correct statement(s) about photoelectric effect.
(A) There is no significant time delay between the absorption of a suitable radiation and the emission of electrons
(B) Einstein analysis gives a threshold frequency above which no election can be emitted
(C) The maximum kinetic energy of the emitted phtotelectrons is proportional to the frequency of incident radiation
(D) The maximum kinetic energy of elections does not depend on the intensity of radiation
59. Half of the space between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor is filled with a dielectric material of dielectric constant K. The remaining half contains air as shown in the figure. The capacitor is now given a charge Q. Then
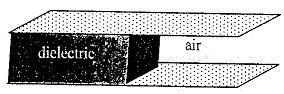
(A) electric filled in the dielectric-filled region is higher than that in the air-filled region
(B) on the two halves of the bottom plate the charge densities are unequal
(C) charge on the half of the top plate above the air-filled part is [tex]\frac{Q}{K+1}[/tex]
(D) capacitance of the capacitor shown above is [tex](1+K)\frac{C_0}{2}[/tex], where [tex]C_0[/tex] is the capacitance of the same capacitor with the dielectric removed
60. A stream of electrons and protons are directed towards a narrow slit in a screen (see figure). The intervening region has a uniform electric field [tex]\vec{E}[/tex] (vertically downwards) and a uniform magnetic field [tex]\vec{B}[/tex] (out of the plane of the figure) as shown. Then
(A) elections and protons with speed [tex]\frac{|\vec{E}|}{|\vec{B}|}[/tex] will pass through the slit.
(B) protons with speed [tex]\frac{|\vec{E}|}{|\vec{B}|}[/tex] will pass through the slit, electrons of the same speed will not.
(C) neither electrons nor protons will go through the slit irrespective of their speed.
(D) electrons will always be deflected upwards irrespective of their speed.
***






