RESISTOR:
![]() Resistor is energy absorbing element in electrical circuit. It's unit is ohm.
Resistor is energy absorbing element in electrical circuit. It's unit is ohm.
The potential difference v across the terminals of resistor R, is directly proportional to the current i flowing through it.
That is,
V=IR; Here R is called the resistance of resistor R
The reciprocal of resistance is defined as conductance( G).
Hence,
(1/R)=G & I=VG
The power absorbed by a resistor is given by
P=VI
INDUCTOR:
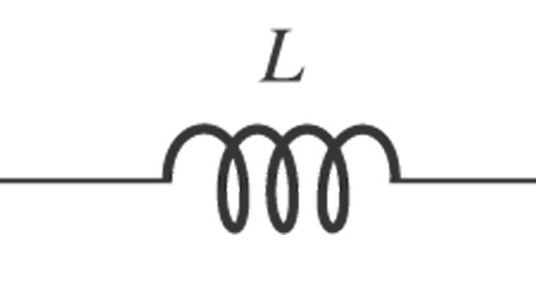 Inductor is an energy storing element in electrical circuit. It's unit is henry.
Inductor is an energy storing element in electrical circuit. It's unit is henry.
The potential difference v across the terminals of inductor is directly proportional to rate of change of current through it.
That is, V=Ldidt; Here the term L is the proportionality constant and known as inductance of the inductor.
Hence, current through inductor is
I=1Lt∫0Vdt+I(0)
Where I(0) is the initial current of the inductor.
The energy stored in an inductor over the interval (t1,t2) is,
E(t1,t2)=t2∫t1VIdt=t2∫t1L(dI/dt)Idt=L2[I2(t2)_I2(t1)]
Inductor store the energy in the form of current.
CAPACITOR:
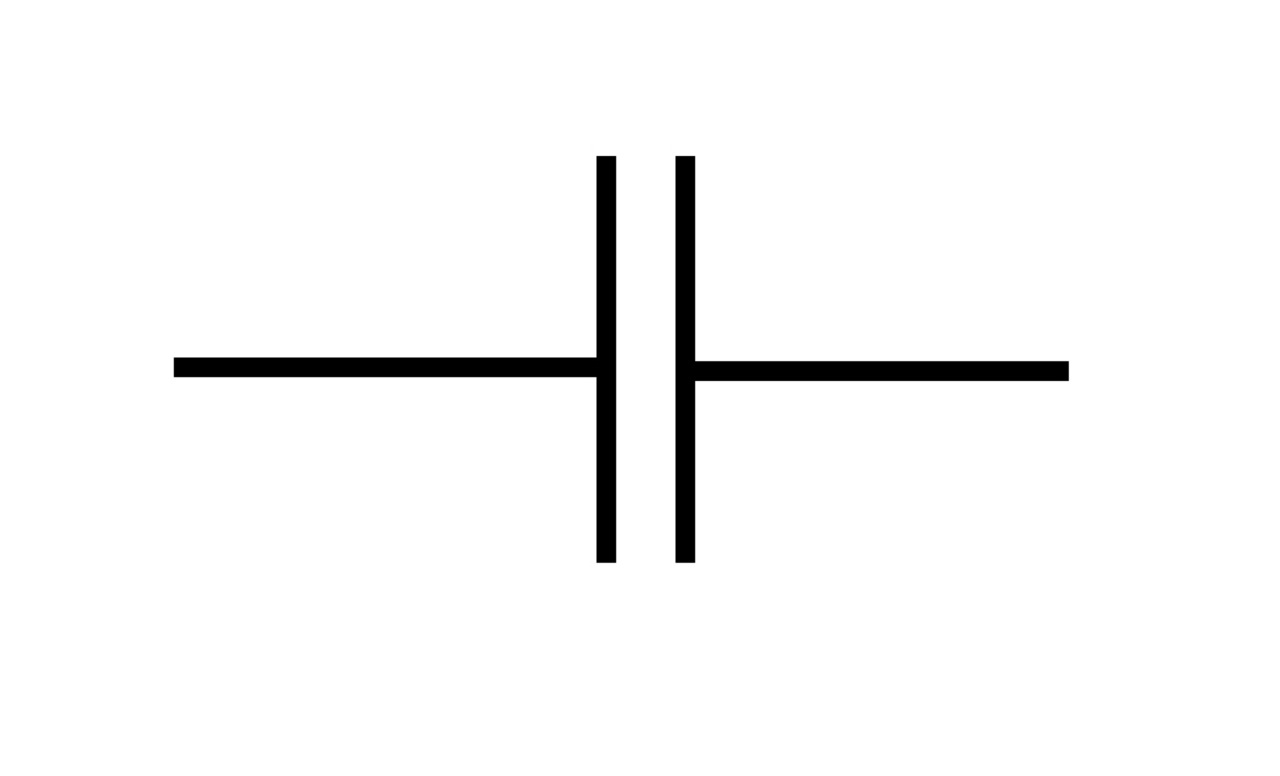 Capacitor is another energy storing element in electrical circuit. It's unit is farad.
Capacitor is another energy storing element in electrical circuit. It's unit is farad.
The potential difference v between the terminals of capacitor is proportional to the charge q on it. That is
v∝q
v=q/C; where C is the proportionality constant and is called the capacitance.
Now, i=dqdt=C(dvdt)
∫dv=1C∫idt
Hence, V(t)=1Ct∫0i(t)dt+q(0)/C
where q(0) is the initial charge across the capacitor C.
The energy stored in a capacitor over the interval (t1,t2) is,
E(t1,t2)=t2∫t1VIdt=t2∫t1VC(dv/dt)dt=C2[V2(t2)_V2(t1)]
Capacitor store the energy in the form of voltage.







