Principle of Transformer
Related Items
Introduction to Electrical Machines
What is Electrical Machines ?
Electrical Machines or Devices is a general term for machines where electromagnetic forces converts into other forms of energy i.e mechanical energy, Electrical Energy, heat, light etc or vice versa.
Direct Current Motors (DC Motors)
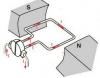
Motor -- a machine converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Construction of D.C motor is similar to D.C generator. Most types produce rotary motion. Another type is Linear motor which directly produces force and motion in a straight line.
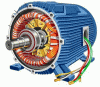
AC Machines
AC Machines
AC machines or Alternating Current Machines are three types by working principles