Kirchhoff's laws simply deal with voltage drops and rises with the current flowing in a circuit by using the ideas of simple energy conservation. These laws are very helpful in determining of the output response for network analysis.
KIRCHHOFF'S LAW:
- Kirchhoff's Voltage law(KVL): The algebraic sum of all branch voltages around any closed loop of a network is zero at all instants of time.
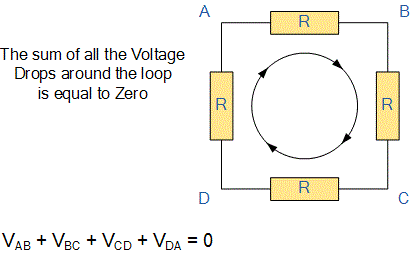 Mathematically kvl can be written as, ∑V=0
Mathematically kvl can be written as, ∑V=0 - Kirchhoff's Current law(KCL): The algebraic sum of the branch currents at a node is zero at all instants of time.
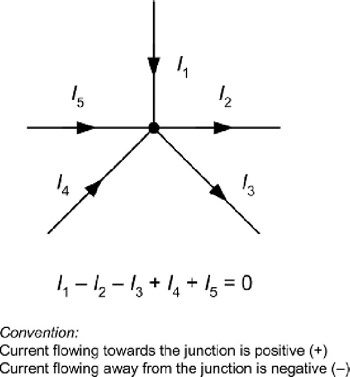
Mathematically kcl maybe written as, ∑i=0
Based on KVL and KCL we can write the loop and node equations respectively.
Example: Let us take a circuit and referring the circuit node and loop equations are written,
Node A Node B
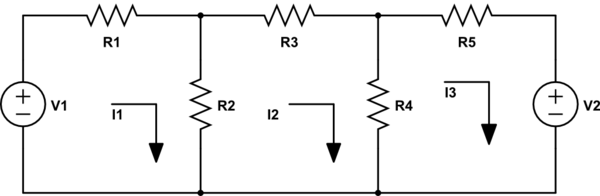
We have three loops and the currents in the elements are as specified. By KVL, we get
I1R1+(I1−I2)R2=V1
(I2−I1)R2+I2R3+(I2−I3)R4=0
(I3−I2)R4+I3R5=V2
Similarly using KCL,the node equations can be written as:
Taking voltage of node A is VA and voltage of node B isVB
(VA−V1)R1+VAR2+(VA−VB)R3=0
(VB−VA)R3+VBR4+(VB−V2)R5=0







