A port is a pair of nodes across which a device can be connected. A network with two input terminals and two output terminals is called a four terminal network or a two-port-network. In a two port network, there are two voltage variables and two current variables.
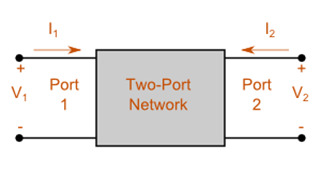
A two-port network is illustrated in figure. External networks that may be connected at the input and output ports called terminals.
In order to describe the relationships among the port voltages and currents of a linear n-port network,'n' number of linear equations are required.Thus for two-port, two linear equations are required among the four variables. However, the choice of two independent and two dependent variables is dependent on particular application.
For n-port network, the number of voltage and current variables is 2n.The number of ways in which these 2n variables can be arranged in two groups of n each is [tex]\frac{{2n!}}{{n! \times n!}} = \frac{{2n!}}{{{{(n!)}^2}}}[/tex] types of port parameter.
For a two port network(n=2) there will be six types of parameters, which are mentioned below:
- Open circuit impedance parameters(z-parameters)
- Short circuit admittance parameters(y-parameters)
- Transmission or chain parameters(T-parameters or ABCD- parameters)
- Inverse transmission parameters(T'-parameter)
- Hybrid parameters(h-parameters)
- Inverse hybrid parameters(g-parameters)
The usefulness, of the different methods of description comes clearly into evidence when the problem is synthesizing or designing networks such as filters,matching networks,wave shaping networks and many others.
- 1017 views






